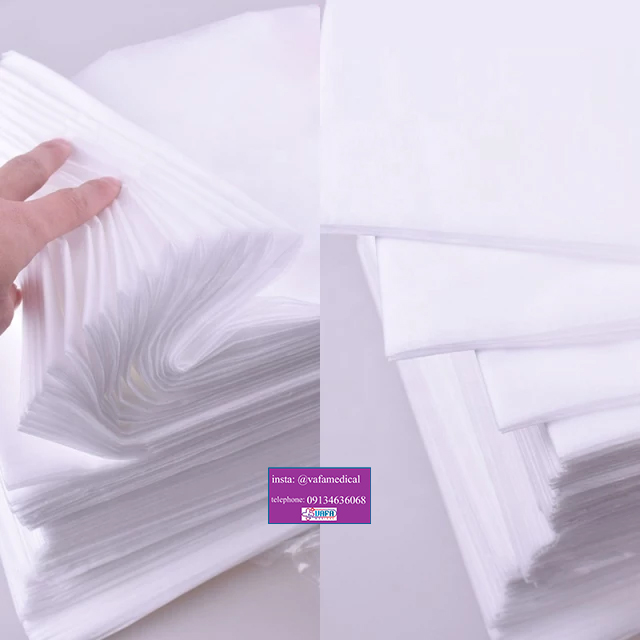
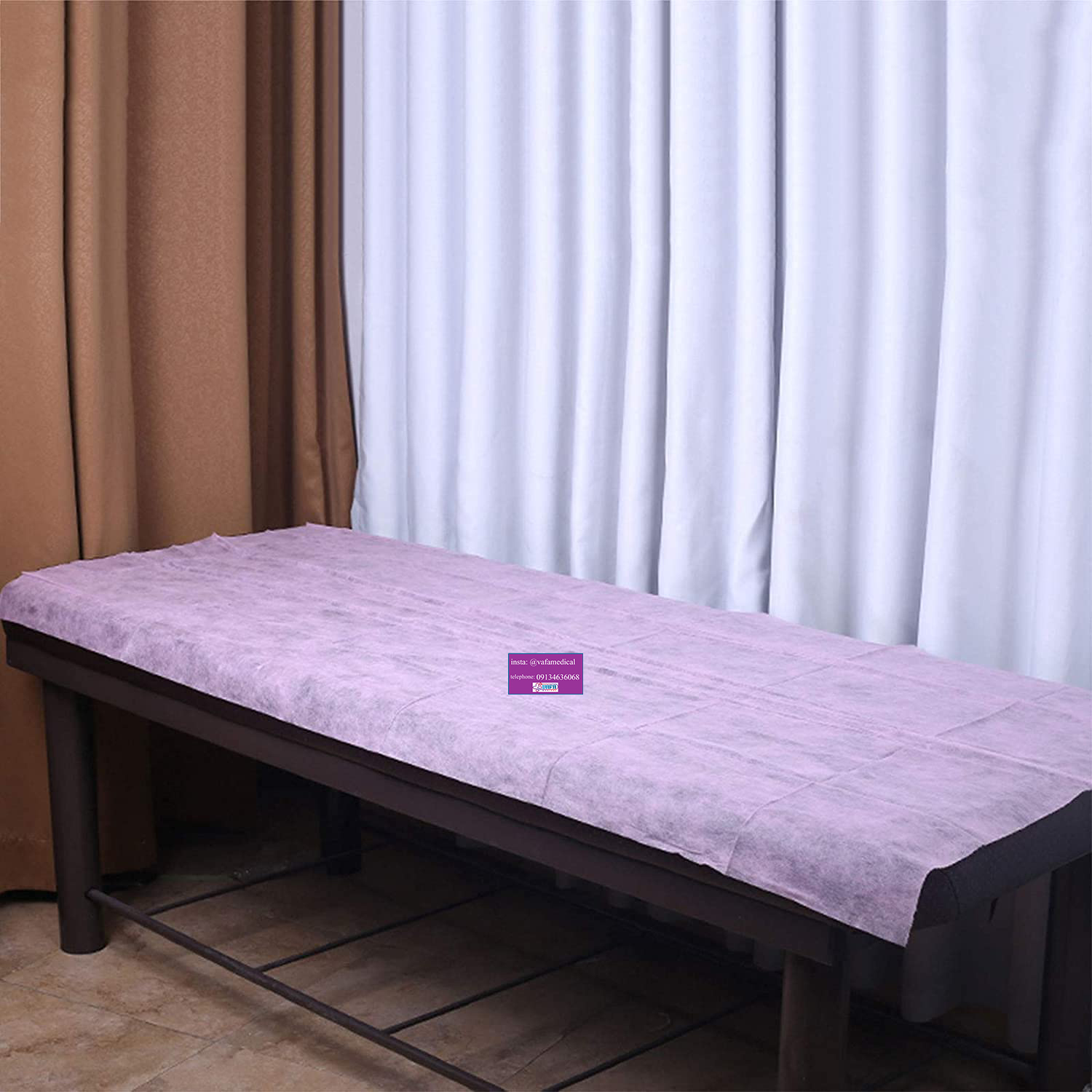
The price of buying disposable Hospital bed sheets from production to consumption in bulk and online is much more affordable than alternative and face-to-face methods.
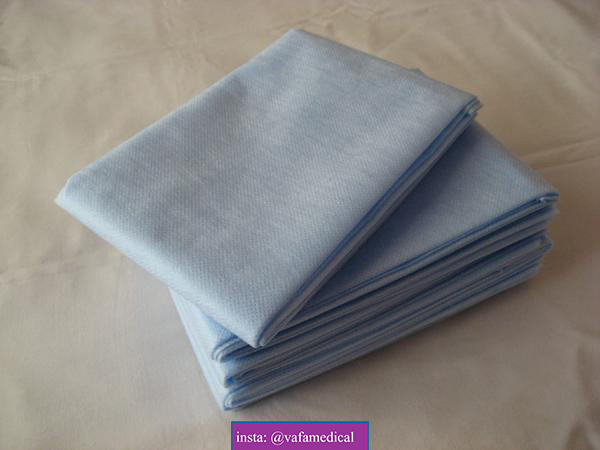

The price of buying hospital bed sheets in bulk, from production to consumption, can vary widely depending on various factors such as the type of sheet, material quality, quantity ordered, customization options, shipping costs, and the supplier’s pricing structure. Here’s a breakdown of the typical cost considerations involved:
- Production Costs: The production cost of Hospital bed sheets includes expenses such as raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, and quality control. Different materials, such as cotton, polyester, or blends, have varying costs. Additionally, specialized features like waterproofing or antimicrobial treatments may incur additional production expenses.
- Wholesale or Manufacturer Pricing: When purchasing in bulk directly from manufacturers or wholesalers, buyers can often benefit from discounted wholesale pricing. The price per unit typically decreases as the quantity ordered increases. Negotiating bulk discounts with suppliers is common and can result in significant cost savings.
- Customization Costs: If customization is required, such as specific sizes, colors, or branding, additional costs may apply. Customization can involve setup fees, design costs, or minimum order requirements. These costs vary depending on the complexity and scale of customization.
- Shipping and Logistics: Shipping costs are a significant consideration when purchasing Hospital bed sheets in bulk, especially if sourcing from overseas manufacturers. Factors influencing shipping costs include distance, mode of transportation, packaging requirements, and any applicable import/export duties or taxes.
- Import/Export Regulations: Compliance with import/export regulations and standards may entail additional costs, such as certification fees, inspection charges, or customs clearance expenses. Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements is crucial to avoid delays and penalties.
- Distribution Costs: If the Hospital bed sheets need to be distributed to multiple locations or stored in warehouses before consumption, distribution costs must be factored into the overall price. These costs may include transportation, storage fees, handling charges, and inventory management expenses.
- Retail Markup: Retailers selling Hospital bed sheets online typically apply a markup to cover their operating expenses, profit margins, and marketing costs. The final retail price may be higher than the wholesale price paid by the buyer.
- Promotions and Discounts: Online retailers often offer promotions, discounts, or bulk purchase incentives to attract customers and encourage larger orders. Taking advantage of these offers can help lower the overall cost of purchasing hospital sheets.
- Currency Fluctuations: For international transactions, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact the final cost of purchasing hospital sheets. Buyers should consider currency hedging strategies to mitigate exchange rate risks.
- Payment Terms: Payment terms negotiated with suppliers, such as upfront payments, installment plans, or trade credit, may affect the overall cost structure. Longer payment terms may provide cash flow advantages but could result in higher financing costs.
To obtain specific pricing information for Hospital bed sheets in bulk, it’s recommended to reach out directly to manufacturers, wholesalers, or online retailers, providing detailed specifications and quantity requirements. Requesting quotes from multiple sources and comparing offers can help identify the most cost-effective solution while meeting quality standards and delivery timelines.
- Production Costs: These include expenses associated with manufacturing the Hospital bed sheets, such as raw materials (fabric, elastic, etc.), labor costs, machinery, utilities, and overhead expenses like rent and insurance. Production costs may also include quality control measures to ensure the sheets meet industry standards.
- Material Costs: The price of materials, such as cotton, polyester, or blends, can significantly impact the overall production cost. Higher-quality materials may incur higher costs but can result in better-performing and more durable Hospital bed sheets.
- Customization Costs: If the hospital sheets require customization, such as specific sizes, colors, or branding, additional costs may arise. Customization costs may include design fees, setup charges, and any additional labor or materials required for customization.
- Packaging Costs: Proper packaging is essential to protect the hospital sheets during transportation and storage. Packaging costs may include the cost of materials (boxes, plastic wrap, etc.), labor for packaging, and any branding or labeling expenses.
- Transportation Costs: Shipping the hospital sheets from the manufacturer to the buyer’s location incurs transportation costs. Factors such as distance, shipping method (sea freight, air freight, trucking), and shipping volume influence transportation costs.
- Import/Export Duties and Taxes: When importing or exporting hospital sheets across international borders, import/export duties, tariffs, taxes, and customs fees may apply. These additional costs vary depending on the countries involved and the classification of the goods.
- Storage and Warehousing Costs: If the Hospital bed sheets need to be stored in warehouses before distribution, storage and warehousing costs must be considered. These costs include rent or lease expenses for warehouse space, utilities, insurance, and inventory management.
- Distribution Costs: Distributing the Hospital bed sheets to end-users or retailers may involve additional costs such as transportation, handling fees, and distribution center expenses. Efficient logistics management can help minimize distribution costs.
- Marketing and Sales Costs: Marketing and sales activities, such as advertising, promotions, trade shows, and sales commissions, contribute to the overall cost of selling hospital sheets. These costs are typically borne by the seller and may influence the final price of the product.
- Retail Markup: Retailers selling hospital sheets online or in-store apply a markup to cover their operating expenses, profit margins, and overhead costs. The retail markup adds to the final price paid by the end consumer.
- Volume Discounts and Negotiations: Bulk purchases often qualify for volume discounts or favorable pricing terms through negotiations with suppliers or manufacturers. Buyers can leverage their purchasing power to negotiate lower prices per unit.
- Currency Fluctuations: For international transactions, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact the final cost of purchasing hospital sheets. Currency hedging strategies may be employed to mitigate the risks associated with currency fluctuations.

To accurately estimate the total cost of purchasing hospital sheets in bulk, buyers should consider each of these cost components and negotiate favorable terms with suppliers or manufacturers. It’s essential to balance cost considerations with quality requirements to ensure the hospital sheets meet the necessary standards for medical use.



